Help for Hair Loss
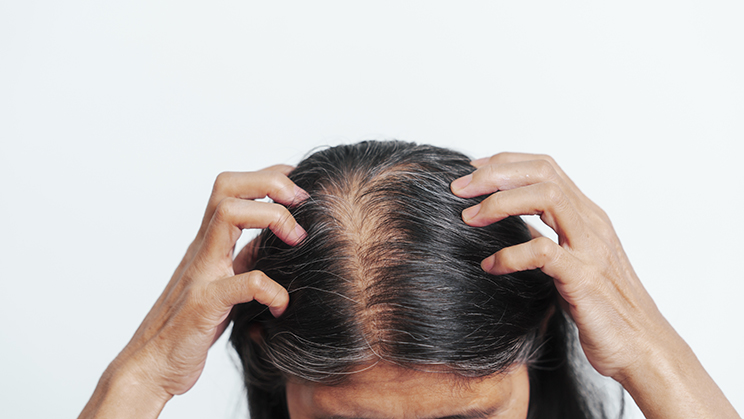

Hair loss is a common problem that can affect both men and women at different stages of life. It can manifest as gradual thinning of hair, large clumps of hair in the brush, or even bald patches on the scalp. The impact of hair loss isn't limited to appearance alone; excessive hair loss can affect self-esteem and cause emotional distress. Hair loss often presents differently in men and women: women typically experience diffuse thinning across the scalp, while men often notice a receding hairline or thinning at the crown.
Hair shedding is normal, with an average of 50–100 hairs falling out daily. However, if hair loss exceeds this amount, there could be an underlying medical, genetic, or environmental cause. This raises questions: What causes hair loss, why is it excessive, and what helps prevent hair loss? Answering these questions and effectively treating the issue requires an understanding of its causes and types.
What Causes Hair Loss?
Hair loss can result from various factors, ranging from lifestyle choices to genetic and hormonal influences. Female hair loss, in particular, is a complex issue that can be linked to estrogen deficiency, nutrient deficiencies, or stress.
- Hormonal Hair Loss in women is often linked to estrogen deficiency, particularly during menopause. A decrease in estrogen can weaken hair growth, leading to thinning at the crown. Hormonal fluctuations after pregnancy can also cause temporary hair loss.
- Telogen Effluvium is a common reaction to physical or emotional stress. Stress can disrupt the hair growth cycle, causing a large number of hairs to enter the resting phase and shed more quickly. Stress-induced hair loss is usually temporary but can persist for months if stress isn't managed.
- Nutrient Deficiencies can also cause hair loss. Hair growth requires adequate vitamins and minerals. For instance, a deficiency in vitamin B12 can impair hair follicle function. Deficiencies in iron, zinc, and vitamin D can also weaken hair quality and lead to shedding.
- In men, hair loss is often related to Genetic Factors and male hormones like DHT. This type, known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common form of permanent hair loss in both men and women.
- Certain Medical Conditions such as hypothyroidism, autoimmune diseases, and anemia can cause significant hair loss. Additionally, side effects from certain medications, such as cancer treatments, may contribute to hair shedding.
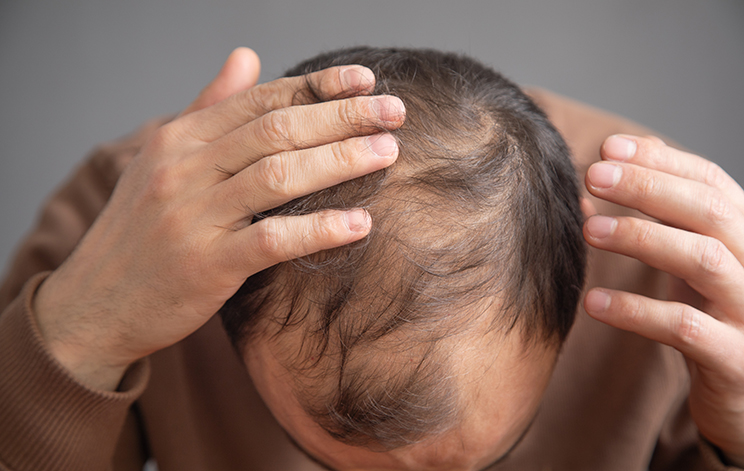

Types and Forms of Hair Loss
Hair loss can manifest in various forms and progress through different stages. Understanding the nature of the symptoms helps in choosing the right treatment.
- Telogen Effluvium: This is the most common temporary form of hair loss where a large number of hairs enter the resting phase and fall out. Causes can include stress, nutrient deficiencies, childbirth, or illness.
- Androgenetic Alopecia, also known as hereditary hair loss, appears as a receding hairline and baldness at the crown in men. In women, it is usually more diffuse and does not necessarily lead to complete baldness.
- Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune disease that causes sudden bald patches on the scalp. In more severe cases, hair loss can spread to the entire body.
- Cicatricial Alopecia: This rarer type occurs when inflammation permanently damages hair follicles. If left untreated, it can lead to permanent baldness.
Although the appearance and severity of hair loss vary individually, it is possible to treat the problem at almost any stage by using the right methods and a tailored treatment plan. Early identification and preventive measures can also help to stop the progression of hair loss and make it easier to manage in the long term.
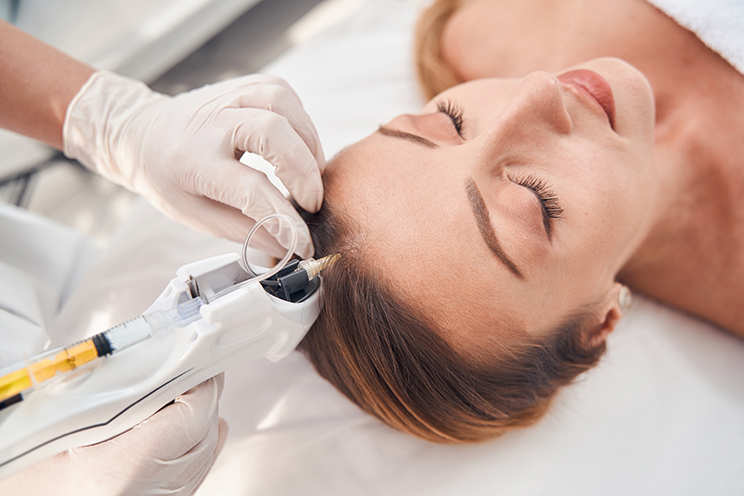
What Helps with Hair Loss?
Looking for solutions for hair loss in women or men? Finding the right treatment can help restore natural hair growth and confidence. Here are some treatment options:
- PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma): This procedure involves injecting the patient's own plasma enriched with platelets. PRP treatment stimulates hair growth in the scalp.
- Mesotherapy: Improves scalp circulation and nutrient supply, strengthening hair follicles, stimulating hair growth, and making the hair look fuller and healthier.
- Minoxidil: An effective hair loss medication that stimulates hair growth. Available as a topical solution or foam.
- Finasteride: A medication for male hair loss that blocks the effect of the DHT hormone and slows hair loss.
- Nutritional Supplements: Deficiencies in B12, iron, and zinc can be corrected with supplements to support hair growth.
- Laser Therapy: Low-level laser therapy stimulates hair follicles and improves blood circulation in the scalp.
- Hormone Therapy: Hormone replacement therapy prescribed by a doctor can help with symptoms caused by estrogen deficiency.
- Hair Transplantation: A surgical procedure where hair is transplanted to balding or thinning areas.
- Stress Management: Reducing stress through practices like yoga or mindfulness can help with telogen effluvium.
MESQ®
DoctusPlus Oy:n aputoiminimi
Yritys
DoctusPlus Oy
Y-tunnus
3154088-6
Käyntiosoite
Itämerenkatu 11-13 F, 00180 Helsinki
Puhelin
Sähköposti
Aukioloajat
Ma – Pe 11:00 – 19:00