Urinary Incontinence and Its Treatment

Urinary incontinence, or incontinence, is a common problem where bladder control weakens, and a person is unable to fully control urination. This condition affects the quality of life, self-confidence, and various social situations, as well as intimate life.
Urinary incontinence can be temporary or persistent, and the severity of symptoms varies from mild leakage to sudden urine loss. Incontinence occurs in people of all ages and both genders, but it is particularly common in women who have given birth and in older men whose pelvic floor muscles may have weakened.
Urinary incontinence is directly related to the function of the pelvic floor muscles and the bladder. The pelvic floor muscles support the bladder, and their strength helps in retaining urine. If the strength of the pelvic floor muscles is weakened, for example, due to childbirth or aging, bladder control is compromised, which can lead to urinary incontinence.
What Causes Urinary Incontinence?
Weakening of the pelvic floor muscles is one of the most common causes of urinary incontinence. The pelvic floor forms support for the bladder, urethra, and intestines, and its muscles play a significant role in normal bladder control. When the muscle structure is firm and strong, it helps to control urination effectively.
In many women, pelvic floor muscles weaken during childbirth, especially in cases of difficult or prolonged delivery. Aging and hormonal changes, such as menopause, also affect pelvic floor muscle function and may increase the risk of urinary incontinence.
In men, weakening of the pelvic floor muscles can be due to prostate surgery. Changes in the pelvic area during surgery can lead to incontinence. Men may also experience urinary incontinence with aging or chronic conditions such as diabetes or obesity, as these factors impact muscle and nervous system function.
Overactive bladder or neurological disorders can also cause urge incontinence, where the bladder suddenly empties without the person being able to control it. This type of urinary incontinence is often more complex and may require long-term treatment.

Different Types of Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence manifests in several different forms, the most common being stress incontinence, urge incontinence, and mixed incontinence.
- Stress Incontinence is related to the weakness of the pelvic floor muscles and typically occurs during physical exertion, such as coughing, laughing, or exercising. In this situation, the pelvic floor muscles are not able to support the bladder sufficiently, leading to urine leakage. Stress incontinence is especially common in women after childbirth, but it can also affect men as they age.
- Urge Incontinence involves an uncontrollable urge to urinate, often due to an overactive bladder. In this type, a person experiences a sudden and strong need to urinate, which they cannot control in time. Urge incontinence is particularly common in older adults and may be influenced by neurological changes or chronic conditions such as diabetes.
- Mixed Incontinence combines features of both stress incontinence and urge incontinence. In this form, a person experiences both urine leakage due to physical exertion and an uncontrollable urge to urinate. In such cases, strengthening the pelvic floor muscles as well as calming the bladder can be beneficial.
- Post-Micturition Dribble, or leakage after urination, is a condition particularly common in men. It is usually caused by insufficient control of the pelvic floor muscles at the end of urination. Although this issue can be bothersome, it is generally treatable with pelvic floor muscle exercises and the correct urination technique.
Urinary incontinence can gradually worsen over time or remain mild and unnoticeable for a long period. Early diagnosis and treatment can help keep the situation under control, and pelvic floor muscle training is an effective preventive measure in most cases.
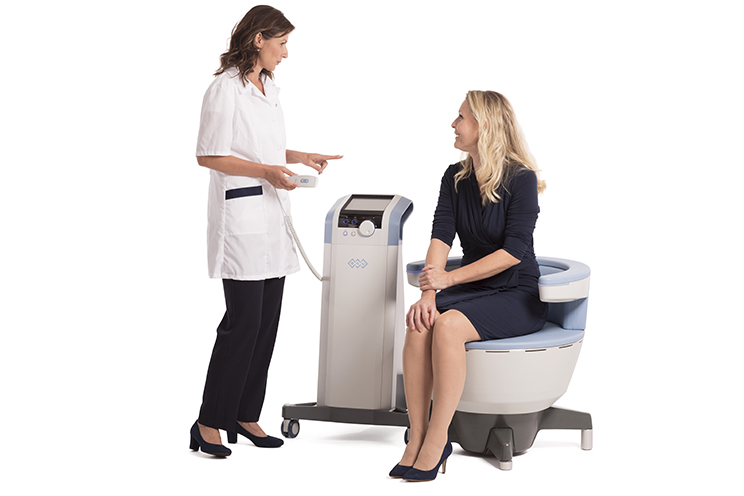
How to Get Rid of Urinary Incontinence?
- EMSELLA Treatment: A specialized device treatment that uses electromagnetic stimulation to strengthen pelvic floor muscles. It is especially suitable for mild to moderate urinary incontinence.
- Pelvic Floor Muscle Training: Regular exercises strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and improve bladder control.
- Pelvic Floor Physiotherapy: Professional-guided physiotherapy focusing on activating and strengthening the pelvic floor muscles.
- Kegel Exercises: Effective exercises targeting the pelvic floor muscles. Kegel exercises are particularly useful in managing stress incontinence.
- Medication: Medication for urinary incontinence may be necessary, especially for urge incontinence. Medications help reduce bladder overactivity.
- Surgical Treatment: In severe cases, surgery may be required. Surgical procedures can correct the structures supporting the urethra and pelvic floor.
Each treatment method plays its role in managing urinary incontinence, and an individualized treatment plan is key to effective rehabilitation.
MESQ®
DoctusPlus Oy:n aputoiminimi
Yritys
DoctusPlus Oy
Y-tunnus
3154088-6
Käyntiosoite
Itämerenkatu 11-13 F, 00180 Helsinki
Puhelin
Sähköposti
Aukioloajat
Ma – Pe 11:00 – 19:00