Ihon pigmenttihäiriö: maksaläiskä, pisamat, vitiligo ja muut
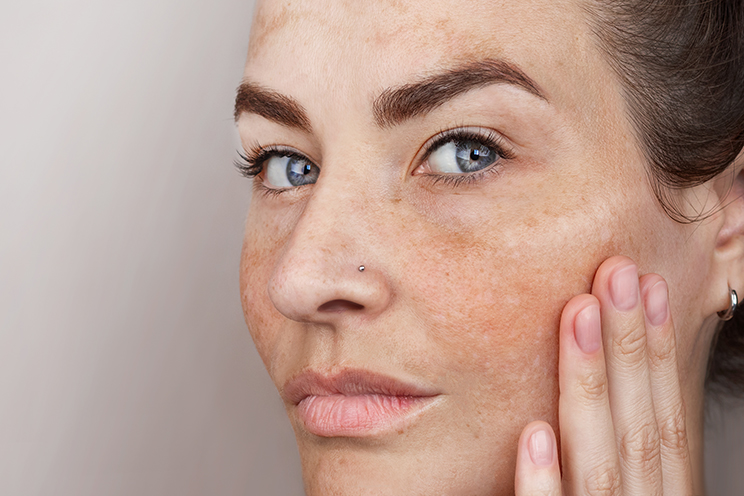

Ihon pigmenttihäiriö tarkoittaa ihon värin ja sävyn muutoksia, jotka johtuvat melaniinintuotannon epätasapainosta. Ihon väri ja sävy määräytyvät perinnöllisten tekijöiden sekä ulkoisten ja sisäisten vaikuttimien perusteella. Kun melaniinia tuotetaan liikaa tai liian vähän, ruskeat läiskät iholla voi muodostua, kuten pigmenttiläiskiä tai vaaleampia alueita.
Pigmentaatiota esiintyy kaikkialla kehossa, mutta se on yleisintä kasvoissa, kaulassa, käsissä ja vartalossa. Pigmentaatio kasvoissa on yksi yleisimmistä ihon epätäydellisyyksistä, ja se voi vaikuttaa itseluottamukseen ja ihonhoitorutiineihin. Pigmentaatio raskauden jälkeen tai auringon jälkeen on erityisen yleistä ja se voi aiheuttaa eriasteisia ihonvärimuutoksia. Lisäksi ympäristön saasteet ja ihon altistuminen haitallisille kemikaaleille voivat lisätä pigmentaation riskiä.
Pigmentaation muodostuminen on yksilöllistä ja se voi riippua esimerkiksi ihotyypistä, iästä ja elämäntavoista. Tummempi iho on luonnostaan alttiimpi hyperpigmentaatiolle, koska siinä on enemmän melanosyyttejä eli soluja, jotka tuottavat melaniinia. Vaaleampi iho puolestaan on herkempi UV-säteilyn aiheuttamille vaurioille ja voi kärsiä herkemmin hypopigmentaatiosta.
Miksi pigmenttihäiriötä syntyy?
Pigmenttiläiskät voivat johtua monista eri syistä. Yleisimmät syyt pigmentaatioon ovat:
- Auringon UV-säteily: Yksi suurimmista syyllisistä ihon pigmentaatiomuutoksiin on auringon ultraviolettisäteily. Auringon jälkeen syntyviä pigmenttiläiskiä kutsutaan aurinkoläiskiksi tai maksaläiskiksi. UV-säteily kiihdyttää melaniinin tuotantoa, mikä voi johtaa ihon epätasaiseen sävyyn ja pysyviin värimuutoksiin.
- Hormonit: Hormonitasojen vaihtelut voivat aiheuttaa hyperpigmentaatiota, erityisesti raskauden aikana tai hormonaalisten lääkkeiden, kuten e-pillereiden, käytön seurauksena. Esimerkiksi melasma eli maksaläiskät ilmenevät usein raskauden aikana tai ehkäisyvalmisteiden käytön myötä.
- Ikääntyminen: Iän myötä ihon kyky säädellä melaniinin tuotantoa heikkenee, mikä voi aiheuttaa tummia läiskiä erityisesti kasvoille ja käsille. Ikääntymisen myötä myös ihon luonnollinen suojamekanismi heikkenee, mikä voi johtaa entistä suurempaan herkkyyteen UV-säteilylle.
- Ihotulehdukset ja arvet: Ihon tulehdukset, kuten akne tai ekseema, voivat jättää tummia pigmenttiläiskiä tulehduksen paranemisen jälkeen. Tulehduksen jälkeinen pigmentaatio voi kestää kuukausia tai jopa vuosia, mikä tekee siitä erityisen hankalan ongelman.
- Geneettiset tekijät: Perimä vaikuttaa siihen, kuinka herkkä iho on pigmentaatiomuutoksille. Esimerkiksi kesakot ja pisamat ovat pitkälti perinnöllisiä ja voivat voimistua auringonvalon vaikutuksesta.
- Lääkkeet ja kemikaalit: Jotkut lääkkeet, kuten antibiootit ja kemoterapialääkkeet, voivat aiheuttaa pigmentaatiomuutoksia. Myös kosmetiikkatuotteet, jotka sisältävät ihoa ärsyttäviä ainesosia, voivat aiheuttaa hyper- tai hypopigmentaatiota pitkäaikaisessa käytössä.
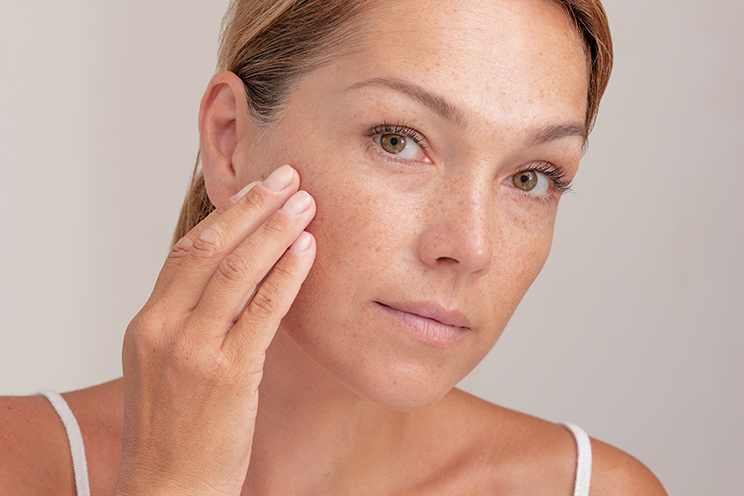

Pigmentaation eri muodot ja vaiheet
Pigmentaatiota on olemassa monenlaista ja se voi esiintyä eri muodoissa ja vaiheissa:
Hyperpigmentaatio
Hyperpigmentaatiossa ihon tietyt alueet muuttuvat tummemmiksi liiallisen melaniinin tuotannon vuoksi. Se voi ilmetä seuraavina muotoina:
- Maksaläiskät (melasma): Yleensä hormonaalisten muutosten tai auringonvalon aiheuttamia tummia läiskiä kasvoilla. Maksaläiskät voivat olla vaikeasti hoidettavia ja vaativat pitkäjänteistä hoitoa.
- Auringon aiheuttamat pigmenttiläiskät: Näitä esiintyy usein kasvoissa, käsissä ja dekolteella. Ne syntyvät yleensä vuosien aikana, kun iho altistuu toistuvasti auringolle.
- Jälkitulehduksellinen hyperpigmentaatio: Ihon tulehduksesta tai aknesta johtuva tummuminen. Tämä on erityisen yleistä niillä, jotka kärsivät aknearpien aiheuttamista pigmenttimuutoksista.
Hypopigmentaatio
Hypopigmentaatiossa ihon pigmentti vähenee ja ihoalueet muuttuvat vaaleammiksi:
- Vitiligo: Autoimmuunisairaus, jossa iho menettää pigmenttiä epätasaisesti. Vitiligossa iholla näkyy vaaleita läikkiä, jotka voivat levitä ajan myötä.
- Jälkitulehduksellinen hypopigmentaatio: Voi syntyä ihovaurioiden tai tulehdusten jälkeen. Ihon vaaleammat alueet saattavat olla tilapäisiä tai pysyviä.
Kesakot ja pisamat
Kesakot ja pisamat ovat luonnollisia ja perinnöllisiä pigmentaatiomuutoksia, jotka voimistuvat auringonvalon vaikutuksesta. Ne eivät ole varsinaisia pigmenttihäiriöitä, mutta niiden voimakkuus voi muuttua vuodenaikojen mukaan. Kesakoiden esiintyminen on yleisempää vaaleaihoisilla henkilöillä, joilla on herkkä iho.
Parhaat hoitomenetelmät pigmenttihäiriöihin
- EXION Clear RF: Poistaa pigmenttiläiskät yhdistämällä radiofrekvenssin ja mikroablaation, jotka yhdessä hajottavat pigmenttiä ja stimuloivat ihon uudistumista.
- PRP-hoito: Toimenpiteellä ei ole suoraa ihoa vaalentavaa vaikutusta, mutta se auttaa tekemään pigmentistä vähemmän näkyvää stimuloimalla solujen uudistumista ja ihon uusiutumista sekä vähentämällä tulehdusta, erityisesti tulehduksen jälkeisessä hyperpigmentaatiossa.
- PRP-hyaluroonihappohoito: Tehokas hoito tulehduksen jälkeiseen pigmentaatioon ja aknearpien häivyttämiseen . Verihiutaleiden kasvutekijät ja hyaluronihappo parantavat ihon sävyä ja rakennetta.
- Mesoterapia: Toimittaa kirkastavia aineita suoraan soluihin ja pigmentoituneille alueille, estäen uuden pigmentin muodostumista sekä tasoittaen ihon sävyä ja parantaen ihon yleistä kuntoa.
- Aesthefill: Stimuloi kollageenin tuotantoa ja vaalentaa ihoa polymmaitohapon vaikutuksen avulla, parantaen ihon sävyä ja rakennetta.
- EMFACE: Veitsetön ja moderni facelift-laitehoito joka parantaa ihon rakennetta ja tasoittaa pigmenttihäiriöitä.
- EXION Face: Käyttää kohdennettua ultraääntä ja monopolaarista radiofrekvenssiä ja stimuloi hyaluronihapon, kollageenin ja elastiinin tuotantoa, auttaen pigmenttiläiskien vaalentamisessa.
- EXION Fractional: Tässä hoidossa yhdistyvät monopolaarinen radiotaajuus RF ja tekoäly yhdistettynä mikroneulaukseen, jotta energiaa voidaan antaa tarkasti ihon syvempiin kerroksiin. Säännöllisesti toteutettuna hoito voi auttaa tasoittamaan ihon pintaa.
- Hydrafacial: Kuorii ihoa hellävaraisesti, poistaa ihon pinnan värimuutoksia ja syöttää ihoon kirkastavia boostereita, jotka tasoittavat ihon sävyä ja parantavat ihon heleää ulkonäköä.
- EXION™ Face + EMFACE™ -yhdistelmä: Hoito, joka mahdollistaa laajemman potilasryhmän tarpeiden täyttämisen: hoitaa ja tyydyttää potilaita kaikista ikäryhmistä, hoitaa potilaita, jotka eivät voi tai halua saada injektioita tai leikkausta, ja se on myös erinomainen täydennys injektioille ja leikkaukselle.
- EXION™ Fractional + EMFACE™: Erinomainen yhdistelmä kasvojen ihon korjaamiseen, kohottamiseen ja kosteuttamiseen. Se palauttaa ihon kiinteyden, joustavuuden ja koostumuksen, samalla kun arvet ja ihon pinta tasoittuvat.
- Ihonhoito: Säännöllinen ihonhoitorutiini sisältäen aurinkosuojan ja kirkastavia ainesosia, kuten C-vitamiinia ja niasiiniamidia.
- Kemiallinen kuorinta: Poistaa ihon pintakerroksen ja stimuloi uuden ihon kasvua, auttaen tasoittamaan ihon väriä.
- Laserhoito: Hajottaa liiallista melaniinia, jolloin tummat pigmenttiläiskät vaalenevat.
- Mikroneulaus: Stimuloi ihon uudistumista ja tasoittaa pigmenttieroja.
- Kirkastavat voiteet ja seerumit: C-vitamiinia, retinolia tai kojic-happoa sisältävät tuotteet.
- Aurinkosuoja: SPF 30-50 suojaa ihoa ja ennaltaehkäisee uusien pigmenttihäiriöiden syntymistä.
MESQ®
DoctusPlus Oy:n aputoiminimi
Yritys
DoctusPlus Oy
Y-tunnus
3154088-6
Käyntiosoite
Itämerenkatu 11-13 F, 00180 Helsinki
Puhelin
Sähköposti
Aukioloajat
Ma – Pe 11:00 – 19:00